-
- Market Research
- |
- CBD Near Me
- |
- Giveaways
- |
- Newsletter
- |
- Contact
- |
- Advertise
- |
Treating Epilepsy with CBD
Epilepsy is a prevalent disease with no cure, prompting the need for novel therapies. As research is indicating, cannabidiol (CBD) may be such a therapy as it has the potential to manage seizures and even prevent them. Furthermore, as a study by world leading cannabis research Raphael Mechoulam notes, CBD is well tolerated and seemingly presents no serious side effects. These promising benefits and good safety profile show CBD is a viable alternative treatment, which may provide epilepsy patients with renewed hope for living a normal life.
An Overview of Epilepsy

According to the Epilepsy Foundation, epilepsy is the fourth most common neurological disorder in the United States, affecting 3.4 million people nationally, including nearly 470,000 children. Additionally, 65 million worldwide have epilepsy.
There are 150,000 new cases of epilepsy each year in America and an estimated one in 26 people in the nation will develop epilepsy at some point in their life. Epilepsy cases grow after age 55 as other conditions associated with age such as Alzheimer’s can cause epilepsy.
Epilepsy is a disease defined as recurrent, unprovoked seizures. Thus, an individual who has one seizure does not necessarily have epilepsy unless he or she has another one or is likely to experience more. Statistically, it is more likely than not that after having one seizure, an individual will have another one.
For example, those who have a seizure from an unknown cause have a 50 percent chance of experiencing another seizure within six months. Those who do know the cause of their initial seizure have an 80 percent chance of another seizure in six months.
During a seizure, many symptoms are possible. These symptoms include:
- Blackouts or passing out
- Feeling confused
- Becoming distracted
- Hearing loss or becoming mute
- Twitching
- Convulsing
- Difficulty breathing
Seizures affect people in different ways, but an individual will usually experience the same symptoms every time. For example, if a patient’s typical seizure symptoms are twitching and becoming distracted, these same symptoms can be expected in subsequent seizures.
However, because of the complexity of the brain, it is always possible for new and different symptoms to appear.
The severity of seizures are usually minor and end on their own; however, more adverse events such as personal injury, medical emergency, or even death can occur.
Anywhere from 22,000 to 42,000 people die in the United States from seizures annually. Some deaths occur from prolonged seizures while others happen randomly, known as sudden unexpected death in epilepsy (SUDEP).
How Epilepsy Works
Before getting into how CBD treats epilepsy, it is important to understand how epilepsy works:
Pathophysiology of Epilepsy
Frequent seizures are the defining characteristic of epilepsy. While the seizures themselves are not a disease, they are a symptom of a serious neurological disorder in the brain.
Seizures happen when a group of neurons give off an abnormal electrical discharge. This is seemingly caused by an imbalance of neurotransmitters in the brain, such as glutamate.
Neurotransmitters are chemicals responsible for carrying messages across neurons, but when there is an imbalance, neurons are either hyperactivated or receive too little activity. In either case, once a large enough group of neurons experiences this imbalance, a seizure occurs.
As research by the Mario Negri Institute for Pharmacological Research in Italy suggests, seizures cause inflammation in the brain and inflammation prompts seizures to return more often and more severely. This positive feedback creates an increasingly damaging cycle in the brain of an epilepsy patient.
During seizures, cytokines (proinflammatory cells produced by the immune system) are released and worsen symptoms. Cytokines also affect the reuptake of glutamate by inhibiting astrocytes (cells which regulate neurotransmitters). The excess glutamate eventually leads to the death of neurons. This makes controlling glutamate a critical factor in managing epilepsy.
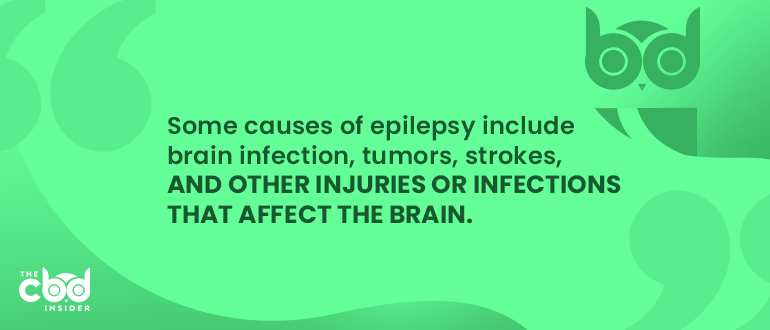
Some causes of epilepsy include brain infection, brain trauma caused by injury, tumors, strokes, and other injuries or infections that affect the brain. However, the direct correlation between these maladies and seizures is not always clear. About half of all epilepsy patients do not know what causes their disease. For those who do not know, their illness is generally thought to be a form of genetic epilepsy, according to the Epilepsy Foundation.
Over 30 epilepsy syndromes are noted by the Epilepsy Foundation. Many of these syndromes are characterized by the types of seizures a patient has. While many kinds of seizures exist, they are put into three main categories:
Generalized Onset Seizures
The first grouping is generalized onset seizures, which are defined as seizures that affect both sides of the brain at the same time.
Motor symptoms include jerking movements (clonic), rigid muscles (tonic), limp muscles (atonic), muscle twitching, and spasms.
Specific to generalized onset seizures are absence seizures which often include staring and do not last more than a few seconds.
Focal Onset Seizures
The second is focal onset seizures: seizures which begin on only one side of the brain.
Motor symptoms include the same possibilities as generalized onset seizures but with the addition of repetitive movements, such as clapping or chewing. Non-motor symptoms usually consist of a change in sensations, emotions, or thinking.
Unknown Onset Seizures
The third is called unknown onset seizures when the beginning of the seizure is unknown or not witnessed by another person.
Motor symptoms are usually tonic-clonic or spasms. Non-motor symptoms are often staring and stillness.
Doctors attempt to diagnosis patients with a specific epilepsy syndrome by understanding what types of seizures they experience and performing tests on their brain waves. If doctors can identify a specific syndrome, it is easier to prescribe the best form of treatment.
Medication
Unfortunately, there is no cure for epilepsy. Medications can help prevent and control seizures but often come with problems of their own. Some side effects include fatigue, nausea, vomiting, headaches, tremors, and sleep disruption.
Since epilepsy is a lifelong battle, long-term side effects of medication can occur and cause severe issues such as mood swings, irritability, paranoia, blood clots, as well as liver, pancreas, and kidney problems.
On the other hand, CBD offers a safer approach to treatment and may be more effective for some people than medication.
Studies Show CBD is Effective Against Epilepsy
The following studies illustrate CBD’s effectiveness in managing seizures and controlling epileptic activity:
CBD Use in Pediatric Treatment-Resistant Epilepsy
A study by the Department of Neurology at Stanford University tested 19 parents who had children with difficult-to-treat epilepsy.
The parents had used an average of 12 drugs to help their child find relief without success.
Using CBD, 16 of the 19 parents saw a significant reduction in seizure frequency. Two of the children were completely seizure-free, eight saw at least an 80% reduction in seizures, and six had a 25-60% decrease in seizures.
The only side effects reported were drowsiness and fatigue. CBD also provided quality of life benefits such as improving the children’s alertness, mood, and sleep.
The study concluded CBD was a promising candidate for treatment-resistant epilepsy.
Chronic Use of CBD in Epilepsy Patients
Another study worked on by Raphael Mechoulam, the world’s leading cannabis researcher, split up 15 patients into two groups, one receiving CBD and the other a placebo.
The trial lasted for four-and-a-half months. After the trial, the group receiving CBD reported four of the eight participants were seizure-free, three other participants found partial improvement, and only one patient found it ineffective.
None of the participants had any adverse side effects to CBD, and no signs of toxicity were found.
CBD-Based Medication Epidiolex for Dravet Syndrome
A Mayo Clinic in Rochester, Minnesota completed a study of seven children with Dravet syndrome, a rare form of childhood epilepsy that is difficult to treat with medication.
The children were split into two groups, one receiving CBD (Epidiolex, the first FDA-approved treatment with a substance from marijuana and for Dravet syndrome) and the other a placebo. The group receiving CBD saw a 39% reduction in seizure frequency, showing promise for CBD as a potential treatment in children with Dravet syndrome.
The children reacted well to CBD, noting sleepiness and loose stools as the only side effects, which were remedied by adjusting dosage. Researchers also found that CBD does not negatively react with most epileptic medications.
How CBD Treats Epilepsy

CBD can address the many complications that arise from epilepsy, especially with CBD’s ability to protect nerve cells, reduce inflammation, increase the body’s natural ability to fight epilepsy, and prevent epileptic activity:
CBD Protects Nerve Cells
As seizures occur in epilepsy patients, neurons are damaged by a host of problems, eventually leading to their death. Some of these problems include oxidation, excess neurotransmitters, and exposure to calcium.
Oxidation creates free radicals which break down neurons. As research indicates, CBD is a powerful antioxidant and reduces oxidative stress on neurons, helping them survive.
Excess neurotransmitters, like glutamate, cause excitotoxicity (the damage and death of nerve cells). Cytokines released by the immune system contribute to the overproduction of glutamate causing neurons to be hyperactivated, resulting in seizures and more neuron death.
CBD inhibits cytokine production, calming neurons and keeping them alive. CBD also activates endocannabinoid receptors to lower the levels of excess neurotransmitters in the synapses, protecting neurons from hyperactivity.
Calcium levels rise in patients with epilepsy because of excess glutamate, causing calcium toxicity in neurons which leads to excitotoxicity. CBD also inhibits the transmission of calcium to neurons, protecting them from calcium buildup.
CBD Reduces Inflammation
Cytokines are major contributors to inflammation. When seizures occur, cytokines and other proinflammatory cells move toward injuries in the nervous tissue, causing chronic brain inflammation. As it persists, subsequent seizures occur more often and with more severity.
Thankfully, CBD has anti-inflammatory properties. CBD activates the CB2 receptors on cytokines to accelerate their deaths and inhibit their production. Consequently, inflammation in the brain decreases, reducing the likelihood of seizures and their potential severity.
CBD Increases the Body’s Natural Ability to Fight Epilepsy
The body has its own system that creates cannabinoid compounds like CBD called the endocannabinoid system. CBD is a phytocannabinoid, meaning it comes from plants.
One endocannabinoid compound that can fight epilepsy is anandamide. Anandamide activates CB1 receptors (receptors which affect the neuronal and psychological aspects of the body) to reduce glutamate in the body and protect neurons from damage.
Anandamide is regulated by fatty acid-binding proteins transporting it to the enzyme which breaks it down. However, CBD can help anandamide last longer by inhibiting the protein from transporting anandamide to its enzyme. This allows anandamide to regulate glutamate and protect neurons longer.
CBD Prevents Epileptic Activity
CBD’s most important benefit is its potential to help prevent seizures.
One way CBD can help prevent seizures is by increasing anandamide levels. As anandamide is increased, excess excitatory neurotransmitters like glutamate are reduced. With less excitatory chemicals in the brain, the likelihood of an abnormal electrical discharge from neurons in the brain causing a seizure is decreased.
Another way CBD prevents seizures is by inhibiting T-type calcium channels. These channels are responsible for the excitability of many neurons. By preventing these channels from hyperactivating neurons, CBD lowers the possibility of a seizure.
CBD was found to inhibit these channels at pharmacologically-relevant concentrations, solidifying its status as a viable treatment for epilepsy.
THC Aids CBD in Treatment

Tetrahydrocannabinol (THC) is one of the most well-known compounds in cannabis apart from CBD. THC is responsible for the “high” commonly associated with cannabis as it combines with the CB1 receptors in the brain. However, when CBD is present in the proper ratio, it can negate these effects by activating the CB2 receptors.
THC provides benefits similar to CBD, yet carries them out in different ways. As a result, adding THC to a CBD-based treatment can provide an extra level of effectiveness.
In treating epilepsy, THC can help prevent seizures when it activates the CB1 receptors. By activating the receptors, THC prevents calcium spikes caused by magnesium deficiency (which can lead to convulsions), a common issue in epilepsy patients. In a study by the University of Minnesota Medical School, THC helped raise magnesium levels which inhibited calcium spikes, reducing excitatory signals in neurons.
CBD Can Help Epilepsy Patients Live a Normal Life
Epilepsy patients face many difficulties throughout their lives aside from seizures. Social, academic, vocational, and personal complications can all arise from this disease, preventing patients from enjoying the daily activities of normal life.
As many people are continually diagnosed with a form of epilepsy, including children, it is imperative to find new therapies that offer relief for those who cannot find it.
Fortunately, CBD is becoming an answer for many people.
Research indicates it is not only effective at addressing the core issues of epilepsy at the cellular level but also safer than medication. Since medication can add to the many issues epilepsy patients already face, an alternative therapy that shows little to no signs of toxicity and mild side effects could be an attractive option for some people.
Epilepsy patients do not have to let their disease rule their lives. They can fight back for the chance at a better life with the hope CBD has provided for some already.
How have you used CBD to treat epilepsy? What were the results you have achieved? Let us know in the comments!
Disclaimer: The content on this site is for informational purposes only. We are not medical experts and nothing should be construed as medical advice. Be sure to speak with your physician before taking CBD or any other treatment.