-
- Market Research
- |
- CBD Near Me
- |
- Giveaways
- |
- Newsletter
- |
- Contact
- |
- Advertise
- |

Just when you thought the storm of three-letter acronyms like THC, CBD, and CBN had ebbed, the pro-cannabis community homes in on another razor-thin distinction between cannabinoids in hopes of a legal workaround: the delta-9 versus delta-8 THC split.
Take a deep breath—we realize there’s a ton of misinformation surrounding everything cannabis right now, but we’re here to help with a clear breakdown of delta-8 tetrahydrocannabinol.
It all starts in the fan-leafed enigma that is the cannabis plant, so let’s begin there.
What Is Delta-8 THC?

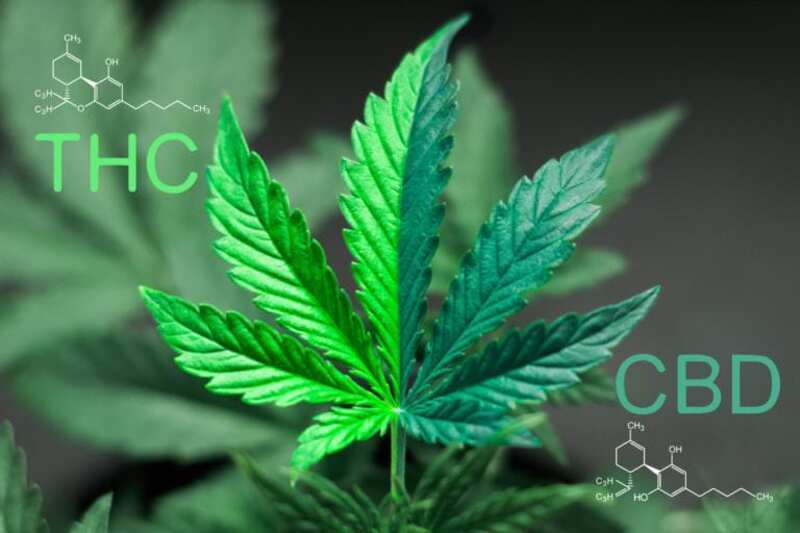
Along with its much more popular cousin, delta-9 THC, delta-8 THC belongs to a class of more than 100 cannabis-based chemical compounds known as cannabinoids (CBD, CBN, CBG, and all the THCs are cannabinoids).
Delta-8 THC is also psychoactive, meaning it can elicit a high when consumed.
However, delta-8 THC is much less abundant in the cannabis plant than delta-9 THC, seldomly rising above a concentration of one percent in unaltered plants.
Selective breeding can increase this number slightly, but the most efficient way to increase the amount is to synthesize delta-8 THC from other cannabinoids (we’ll get to that in a moment).
What Are the Purported Benefits of Delta-8 THC?
According to this PubChem information sheet on the compound, delta-8 THC can help with:
- Nausea and vomiting
- Stress
- Low appetite
- Pain
- Nerve tissue damage and dysfunction
The majority of its interactions with the nervous system take place at the CB1 receptor, of which it is an agonist (stimulator).
The CB1 and CB2 receptors, the compounds that interact with them, and the enzymes that break these compounds down are collectively referred to as the endocannabinoid system.
The THC cousins, CBD, CBN, and all those other cannabinoids work because the body already has this system in place, including our very own brand of internally produced cannabinoid, anandamide.
Delta-8 THC stimulates CB1 (and to a lesser extent, CB2), which contributes to dozens of physiological processes that support the above benefits.

Delta-8 THC Side Effects
Lighthearted pop culture references aside, delta-8 THC side effects can potentially progress beyond the “munchies.”
Yes, it’s a naturally occurring compound, but so is arsenic.
A study by Shaare Zedek Hospital in Jerusalem examining the efficacy of delta-8 THC as an anti-nausea treatment for children with cancer noted the following side effects:
- Dizziness
- Euphoria
- Fatigue
- Irritability
As with all compounds and/or drugs, quantity, co-administration of other meds or alcohol, medical history, and several other factors can affect risk factors for side effects.
Now to address the elephant in the room: how is delta-8 THC similar to and different from delta-9 THC?
For starters, the above side effects are much less frequent and potent with delta-8 THC.
Similarities and Differences Between Delta-8 and Delta-9 THC
Press coverage is just the beginning when it comes to the several differences between these compounds, and at the same time, they are similar in many regards.
First and foremost, they’re made of the same stuff, but built differently.
Chemical Structure
Both of these cannabinoid molecules contain the exact same number of the exact same elements; the chemical formula for delta-8 THC and delta-9 THC is C21H30O2
However, the way the atoms bond to each other is slightly different.
Where delta-9 THC has a carbon-to-carbon double bond on the ninth carbon atom, delta-8 THC has a carbon-to-carbon double bond on the eighth carbon atom.
These two molecules are what chemists refer to as isomers or structural analogs of each other: molecules composed of the same atoms, but structured differently.
Though this difference seems tiny, it actually gives delta-8 THC more stability, increasing the molecule’s shelf life and resistance to oxidation.
Potency
In addition to being far less abundant than delta-9 THC, delta-8 is also significantly less potent.
Its interactions with both CB1 and CB2 receptors elicit smaller responses (e.g., pain-controlling effects, anti-nausea effects, etc.) than delta-9 THC.
Recreational and more functionally minded users who prefer a milder high can turn to delta-8 THC, where those in either camp who prefer/need stronger effects may gravitate to delta-9 THC.
Absorption: How, Where, and How Fast
Finally, there is almost no discernible difference between the “pharmacodynamics” of delta-8 and delta-9 THC; both follow the same pathway in the body.
This means that they interact with the same receptors (CB1 and CB2), get metabolized by the same liver enzymes, and are excreted in the same way.
For anyone interested in the fine print, this study from Hokuriku University in Japan breaks it down by the enzyme.
Of course, there are a few discrepancies between how the two compounds are absorbed, but they’re so small, it’s safe for our purposes to consider them negligible.
Legality
The 2018 Farm Bill explicitly excludes products containing more than 0.3% THC from the definition of industrial hemp, i.e., federally legal hemp.
Despite its functional and structural similarity to delta-9, delta-8 THC is not explicitly outlawed by this legislation.
However, here’s the problem: that rule was only pertaining to compounds naturally present in the hemp plant.
In the case of delta-8, for manufacturers to reach desirable quantities of the compound, they have to synthesize it from CBD.
An Interim final rule enacted in August of 2020 by the DEA states that “The AIA (Farm Bill) did not impact the control status of synthetically derived tetrahydrocannabinols because the statutory definition of ‘hemp’ is limited to materials that are derived from the plant cannabis sativa L.”
The rule went on to expand, “All synthetically derived tetrahydrocannabinols remain schedule I controlled substances.”
In other words, the substance itself is technically federally legal in its own right, but the process used to synthesize it renders it illegal.
Key Takeaways

If you’ve skimmed to the bottom in hopes of a TL;DR breakdown, you’re in luck.
Here’s your bite-sized introduction to delta-8 THC, including its similarities and differences to delta-9 THC:
Composition: The chemical formula for delta-8 THC (C21H30O2) is the exact same as delta-9 THC, but the two molecules differ in the location of a carbon-carbon double bond.
Stability and Potency: Though delta-8 THC is less potent than delta-9 THC in all regards (feeling high and experiencing health benefits), its structure allows for greater stability, meaning it can last longer and endure more abuse before breaking down or oxidizing.
Absorption: Both delta-8 THC and delta-9 THC follow almost the exact same pathway in the body, interacting with the same receptors and enzymes.
Legality: While delta-8 THC is technically not a schedule I controlled substance like THC-containing marijuana, the process of synthesizing it (as is required to achieve therapeutic quantities) lumps it in with schedule I substances.
That’s one misrepresented cannabinoid down, a hundred more to go.