-
- Market Research
- |
- CBD Near Me
- |
- Giveaways
- |
- Newsletter
- |
- Contact
- |
- Advertise
- |

Alzheimer’s is a difficult disease to treat, prompting new therapies to be developed. One such therapy is cannabidiol (CBD). In a 2016 study, Israeli scientists — the world’s leading cannabis researchers — suggested medical cannabis oil (which contains CBD) as a promising alternative option for the treatment of Alzheimer’s. CBD is truly changing the perspective on Alzheimer’s disease, providing hope for a diagnosis that can seem hopeless.
An Overview of Alzheimer’s Disease

Alzheimer’s disease is the most common form of dementia, making up 60 to 80 percent of dementia cases. According to the National Institute of Aging, Alzheimer’s is the sixth leading cause of death in the United States, and an estimated five million people are currently affected. About 13 percent of people 65 years or older and around 45 percent over 85 have Alzheimer’s.
The disease often leads to death within ten years because of complications associated with the disease.
Alzheimer’s is a progressive neurodegenerative disease, meaning that it causes deterioration in the neurons in the brain and worsens over time. As a result, Alzheimer’s patients may experience loss of memory, reduced cognitive function, language issues, delusions, and unpredictable behavior.
Studies show Alzheimer’s can begin more than a decade before a patient experiences symptoms. With current medical technology, the disease is nearly impossible to detect before symptoms appear, but scientists are exploring methods of early detection.
Unfortunately, Alzheimer’s has no cure, but medication may be helpful in managing symptoms and slowing its progression.
However, medication may lose its effectiveness, and can also add other complications such as gastrointestinal problems including nausea and diarrhea, fatigue, loss of appetite, irritability, and headaches. Long-term side effects consist of convulsions, increased risk of stroke, and heart, liver, and kidney problems.
How Alzheimer’s Works
Alzheimer’s disease is currently attributed to two main occurrences: the buildup of beta-amyloid protein within brain cells and tangles of the tau protein.
The beta-amyloid protein builds plaques in between brain cells, also called senile plaques. Normally, beta-amyloid plaques are common as people age; however, these plaques are bigger and more abundant in a brain with Alzheimer’s. The plaques destroy the connections between brain cells, eventually causing them to die. This damage begins in the part of the brain responsible for memory called the hippocampus, which is why memory loss is one of the first signs of Alzheimer’s.
Tau protein is normal in nerve cells. Tau helps the transmission of information between nerve cells by stabilizing the pathways. However, tau proteins fill with phosphate and break down in Alzheimer’s patients, destabilizing pathways and connecting with other tau protein to form tangles which disrupt neuronic function.
The combination of these plaques and tau tangles inflict serious damage on the brain, causing it to shrink as the tissue is destroyed. These plaques and tangles evoke an immune system response as well. The immune system “eats” the disabled neurons and causes inflammation in the process, worsening the effects of the disease.
Unfortunately, there is no known cause for these abnormalities. Environment, diet, genetics, lifestyle, and overall health are being explored as possible contributors. Research suggests a healthy diet, exercise, and social engagement may reduce the risk of developing Alzheimer’s.
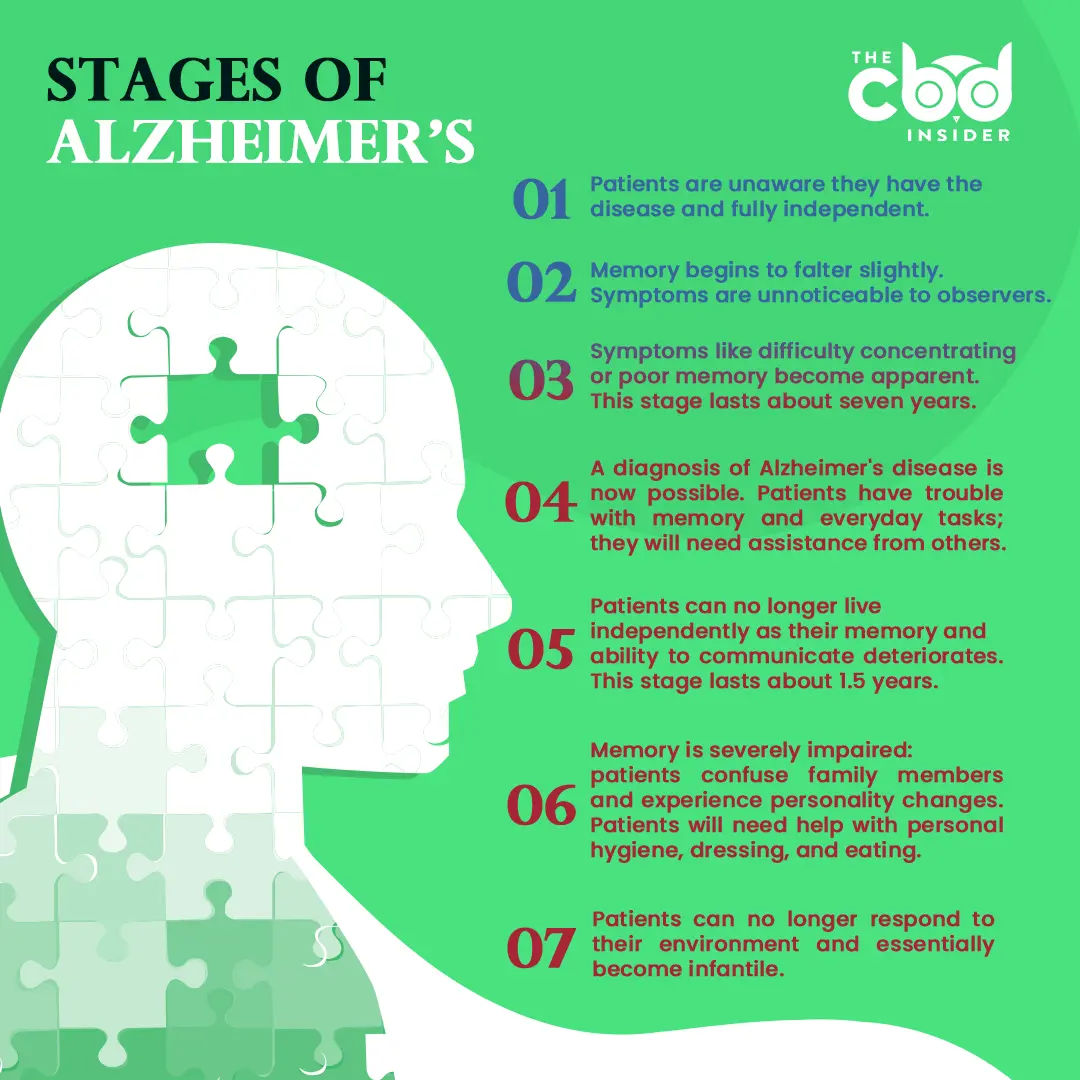
Alzheimer’s Progression
Disease progression may vary person to person, but patients generally experience seven distinct stages:
- Stage 1: Alzheimer’s patients will not know they have the disease as they are fully independent. However, as mentioned before, Alzheimer’s can begin in the brain up to decades before symptoms become noticeable.
- Stage 2: Patients will display normal forgetfulness for their age, but the memory of those with Alzheimer’s will decline quicker than those without. Often symptoms at this age are unnoticeable to observers, but they generally include forgetting words or misplacing objects.
- Stage 3: This stage lasts about seven years, but symptoms become apparent to those close to the patient around two to four years. Patients may have trouble concentrating or forget things they just read. Some people may have to stop working.
- Stage 4: A diagnosis of Alzheimer’s disease is now possible. Patients have trouble with some everyday tasks, may forget memories from their personal life, and show limited emotional responses.
- Stage 5: This stage lasts 1.5 years and patients need lots of support. They will forget major events, their current address, and can no longer live independently.
- Stage 6: Memory is severely impaired to the point where patients will confuse family members, experience personality changes, and become paranoid. They will also need help with personal hygiene, dressing themself, and eating.
- Stage 7: Severe Alzheimer’s has set in and occurs in phases that may last a couple years. Speech will become limited to simple sentences and may decrease to only single recognizable words. Patients may be unable to sit up on their own or hold up their head. Patients essentially become infantile.
Thankfully, research conducted by scientific institutions has found CBD may be an effective and safe alternative treatment to slow this progression and improve the quality of life of Alzheimer’s patients.
Studies on CBD Treating Alzheimer’s Disease
Fortunately, studies are finding that CBD may be effective at reducing memory impairments, protecting brain cells, decreasing inflammation, and slowing the progression of Alzheimer’s:
Medical Cannabis Oil for Alzheimer’s Patients
An open label study by Tel-Aviv University and Bar-Ilan University in Israel tested the efficacy and safety of medical cannabis on ten Alzheimer’s patients for four weeks with medical cannabis oil (the oil also contained some level of THC, the psychoactive compound in cannabis).
After the trial, the study used the Clinical Global Impression (CGI) severity scale (a scale which determines the severity of a patient’s illness) and the Neuropsychiatric Inventory (NPI) (the NPI is used in dementia trials to record psychiatric symptoms) to assess the results. Both scales revealed significant reductions in disease severity, as the CGI score decreased from 6.5 to 5.7 and the NPI decreased from 44.4 to 12.8. The NPI saw a major decrease in delusions, aggression, irritability, and apathy.
No side effects were recorded, and the study concluded medical cannabis is a promising and safe form of treatment for Alzheimer’s.
Testing CBD as a Neuroprotective
A study conducted by the University of Naples Federico II in Italy tested the neuroprotective effect of CBD.
A portion of a group of nerve cells were treated with CBD while another portion was left alone. Afterward, each group of cells was introduced to the beta-amyloid protein.
The portion of cells not treated with CBD were damaged from the protein’s toxicity. However, the cells treated with CBD had a significantly higher survival rate, demonstrating CBD’s neuroprotective properties.
Cannabis-Based Medicine for Late Stage Alzheimer’s
The Universitat de Barcelona and the Carlos III Health Institute in Spain treated mice in the severe Alzheimer’s stage with CBD.
The study concluded that even at an advanced stage CBD could reduce memory impairments.
Evaluating CBD’s Anti-Inflammatory Effects Against Beta-Amyloid
The University of Rome La Sapienza performed a study treating mice that were induced with beta-amyloid. The introduction of the beta-amyloid protein caused inflammation in the neurons.
When CBD was administered, the study found that it decreased inflammation significantly and hindered the production of beta-amyloid, keeping inflammation at bay.
How CBD Treats Alzheimer’s
It seems that CBD directly addresses the two major role players of Alzheimer’s: beta-amyloid protein plaques and tau tangles. Doing so reduces symptom severity and slows down the progression of Alzheimer’s, giving patients hope for a higher quality of living.
| BENEFIT | HOW CBD HELP |
| CBD Prevents Disease Progression | CBD is an antioxidant and protects the brain from deterioration |
| CBD Protects Neurons | CBD removes beta-amyloid and inhibits its reappearance |
| CBD Reduces Neuroinflammation | CBD reduces levels of cytokines in brain cells |
| CBD Helps the Brain Heal | CBD promotes neurogenesis and increases neurotrophin levels |
The following are the possible benefits of CBD:
CBD as a Preventative
Since Alzheimer’s is a progressive illness with no current cure, the most important goal is to prevent progression. As the disease worsens, so does a patient’s quality of life and life expectancy.
This progression is likely led by beta-amyloid, the formation of tau tangles, and inflammation. Each of these contribute to the death of nerve cells and brain tissue.
As the University of Naples Frederico II study suggests, CBD appears to have neuroprotective properties. These properties give neurons a greater chance of survival against beta-amyloid and tau tangles by activating the CB receptors in the brain. As CBD activates these receptors, tau collapses are prevented, maintaining their stability for longer.
Oxidation is another source of Alzheimer’s progression. Oxidative stress is increased in a brain with Alzheimer’s and it interferes with the normal function of the mitochondria in cells (mitochondria are the digestive system of cells and provide energy).
However, CBD has powerful anti-oxidant properties. By eliminating free radicals in the brain and nervous system, CBD reduces oxidative stress and allows cells to function properly again.
These protective effects make CBD promising as a preventative measure against disease progression.
CBD Removes Beta-Amyloid
According to medical experts, beta-amyloid seems to cause cell death and damaging inflammation.
However, after a study done by the Salk Institute, CBD and other cannabinoids were found to remove beta-amyloid plaques within brain cells, allowing the cells to survive. This can help cause a reduction of Alzheimer’s symptoms in patients and possibly even prevent further progression of the disease.
CBD also helps raise the levels of endocannabinoids (cannabinoids the body makes naturally) which protects nerve cells from further beta-amyloid exposure.
In addition to removing the toxic protein, CBD also inhibits the return of beta-amyloid. The University of Rome La Sapienza study about beta-amyloid-induced mice demonstrated CBD could impair the synthesis of proteins like beta-amyloid, reducing beta-amyloid levels in the brain and helping slow Alzheimer’s progression.
CBD Reduces and Inhibits Inflammation
As beta-amyloid plaques form they cause inflammation. The immune system adds to the inflammation by sending proinflammatory cells called cytokines which attack the abnormalities in the brain cells. This results in severe damage and the eventual death of the cells. Since worsening inflammation promotes disease progression, reducing inflammation is a top priority in treatment.
CBD activates the CB2 receptors on immune cells which help regulate the immune system’s response. CBD inhibits the release of proinflammatory cells and accelerates the natural death of existing ones. Reducing and controlling inflammation allows CBD to remove more beta-amyloid plaque, slowing the progression of Alzheimer’s.
CBD Helps the Brain Heal

While the effects of Alzheimer’s are considered irreversible, a certain level of healing may be achieved.
As shown above, CBD gives brain cells a higher chance of survival against the beta-amyloid plaques and tau tangles that damage the brain. While addressing these problems, CBD also promotes the natural healing mechanisms of the brain.
CBD helps the brain heal in two ways. First, it bolsters the number of neurotrophins in the brain. Neurotrophins are proteins that help neurons survive and develop. They protect neurons from the damaging effects of Alzheimer’s while also helping new neurons develop.
Second, CBD also supports neurogenesis. Neurogenesis is the process of neurons being born from stem cells, including their growth and development. Helping the brain create new nervous tissue prevents the brain from shrinking, maintaining and possibly improving cognitive function.
The healing properties of CBD may help Alzheimer’s patients regain a level of cognitive function and maintain that level for some time.
THC May Aid CBD in Treatment
Tetrahydrocannabinol (THC) is another compound of cannabis, best known for producing the “high” associated with the plant. However, when combined with CBD in correct ratios, its psychoactive properties are negated.
THC binds with a different cannabinoid receptor than CBD called the CB1 receptor. CB1 receptors are abundant in the brain and are responsible for regulating memory processes and other aspects of cognitive function. Thus, adding THC to CBD may create an even more effective treatment, especially in Alzheimer’s.
THC does many of the same things CBD does when addressing Alzheimer’s. Research shows THC is effective at removing beta-amyloid plaque formations and can reduce the protein’s overall levels. It also suppresses the immune system’s proinflammatory response, helping to prevent the progression of the disease.
A study on THC by the University of South Florida tested THC’s effectiveness on cells induced with beta-amyloid. After providing extremely small doses of THC to the cells and observing them over time, the cannabinoid compound was found to significantly lower the beta-amyloid levels.
In the same study, THC also prevented tau proteins from filling with phosphate, meaning it may stop tau tangles from forming. The study concluded THC was effective, did not present any toxicity, and is a viable treatment option for Alzheimer’s.
A unique effect of THC is promoting levels of acetylcholine, an important neurotransmitter that maintains healthy memory function.
The enzyme which breaks it down is called acetylcholinesterase, and in Alzheimer’s this enzyme speeds up the creation of the beta-amyloid plaques. THC can inhibit the enzyme and allows acetylcholine levels to rise while simultaneously preventing the creation of beta-amyloid plaques.
CBD May Improve Quality of Life for Alzheimer’s Patients
Current Alzheimer’s medications are limited in their effectiveness to manage the symptoms of the disease and prevent its progression. Coupled with the prevalence of Alzheimer’s in America, it is more important than ever that new, effective therapies are discovered.
Thankfully, research is steadily proving CBD to be a promising treatment for Alzheimer’s patients. As clinical trials show, patients have found reduced disease severity, extended life expectancy, and improved quality of life.
The research also shows CBD can reduce symptoms, improve memory and cognitive function, impede the progress of Alzheimer’s, and may present a safer alternative to medication. As a result, patients and their families can enjoy normal life for longer without the fear of harmful side effects.
There is hope for sustaining a functional lifestyle with CBD!
If you’ve used CBD for the treatment of Alzheimer’s disease with yourself or a family member, let us know what you achieved in the comments below!
Disclaimer: The content on this site is for informational purposes only. We are not medical experts and nothing should be construed as medical advice. Be sure to speak with your physician before taking CBD or any other treatment.





3 Comments
Started my mom who has moderate/ severe dementia. She has been on CBD oil (20 mg/1ml of cbd for 1 week. She is steadier when walking, she can get down the stairs better, she has colour in he face her eyes are bright less jaundice. I can’t wait to see the affects with longer use.
Please keep us informed! You can reply back to this comment or email us through our contact form.
Hi Cindy,
Any updates since your last post? My dad has just been diagnosed. We were strongly considering an alternative medicine.
Could you email me? [email protected]
Thank you very much!
Matt